For the fourth consecutive year, Finland was named the happiest country in the world in the 2021 World Happiness Report. The annual report, released by the United Nations Sustainable Development Solutions Network, ranks countries according to national happiness in addition to providing in-depth reports on specific areas of happiness and well-being.
The United States dropped one more spot in the rankings, from No. 18 last year to the 19th spot for 2021. Five years ago, the U.S. ranked 13th. The lowest-ranking countries were Rwanda, Zimbabwe, and Afghanistan.
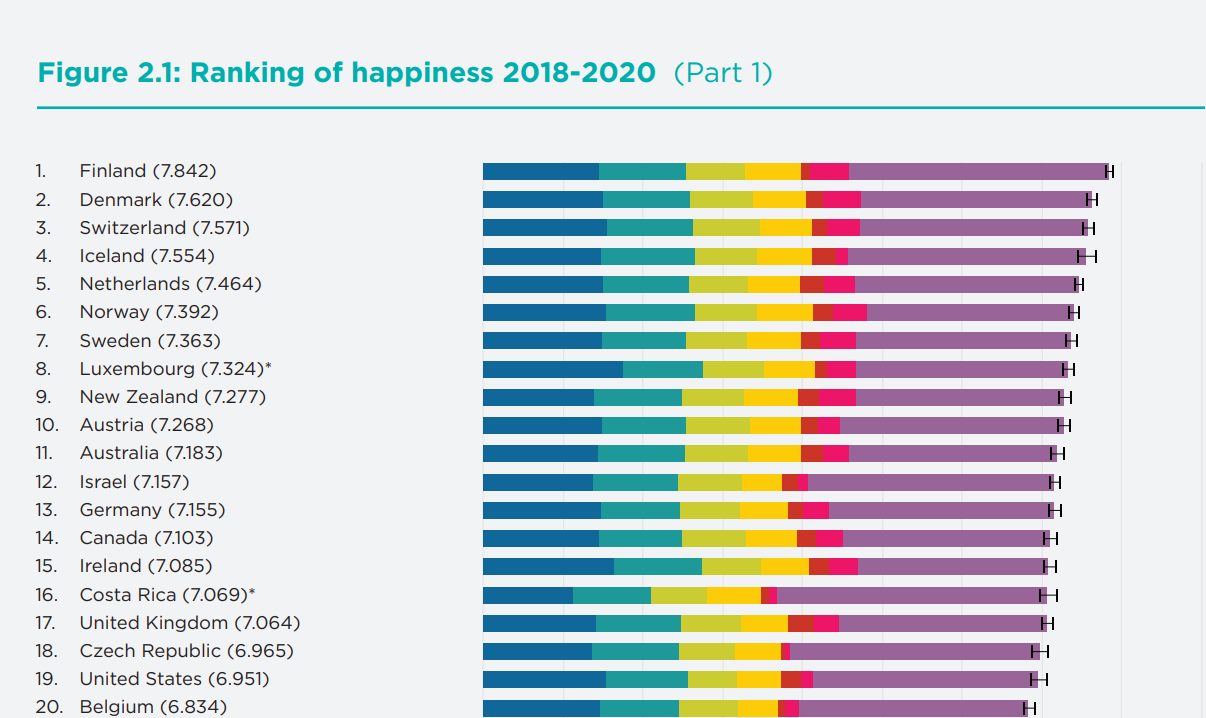
The World Happiness Report has been produced every year since 2012 and uses data gathered by the Gallup World Poll. This year’s editors are John F. Helliwell, Richard Layard, Jeffrey D. Sachs, Jan-Emmanuel De Neve, Lara B. Aknin, and Shun Wang.
While introducing the report during a workshop on Saturday, March 20 — the International Day of Happiness — Sachs noted that 2020 presented “the strangest year in producing the World Happiness Report.”
“We were trying to understand and monitor in real-time incredibly complex challenges and changes,” he said. “The impacts of COVID-19 have differed so widely across different groups in society.”
He added that as the pandemic continues unfolding, the report provides an analysis and snapshot of a complicated story.
Understanding the Impact of COVID-19
This year’s report looked specifically at how the global coronavirus pandemic affected happiness and well-being around the globe. Not surprisingly, survey respondents reported their mental health was affected by COVID-19, and that decline was seen around the world. The UK, for example, reported a 47% increase in mental health problems.
Globally, women, young people, and poorer populations were hit harder by the pandemic. The problem was exacerbated by the disruption of mental health services in many countries just when they were needed most. However, report authors noted, the positive effect is that more attention is being given to mental health and this increased awareness could pave the way for more research and better mental health services.
One of the biggest impacts on happiness and well-being has been the lack of social connection during COVID-19. Due to physical distancing, lockdowns, and self-isolation, people had fewer opportunities to connect with others. Feelings of connectedness to others were related to levels of happiness, and when less social support was available, loneliness increased and happiness fell.
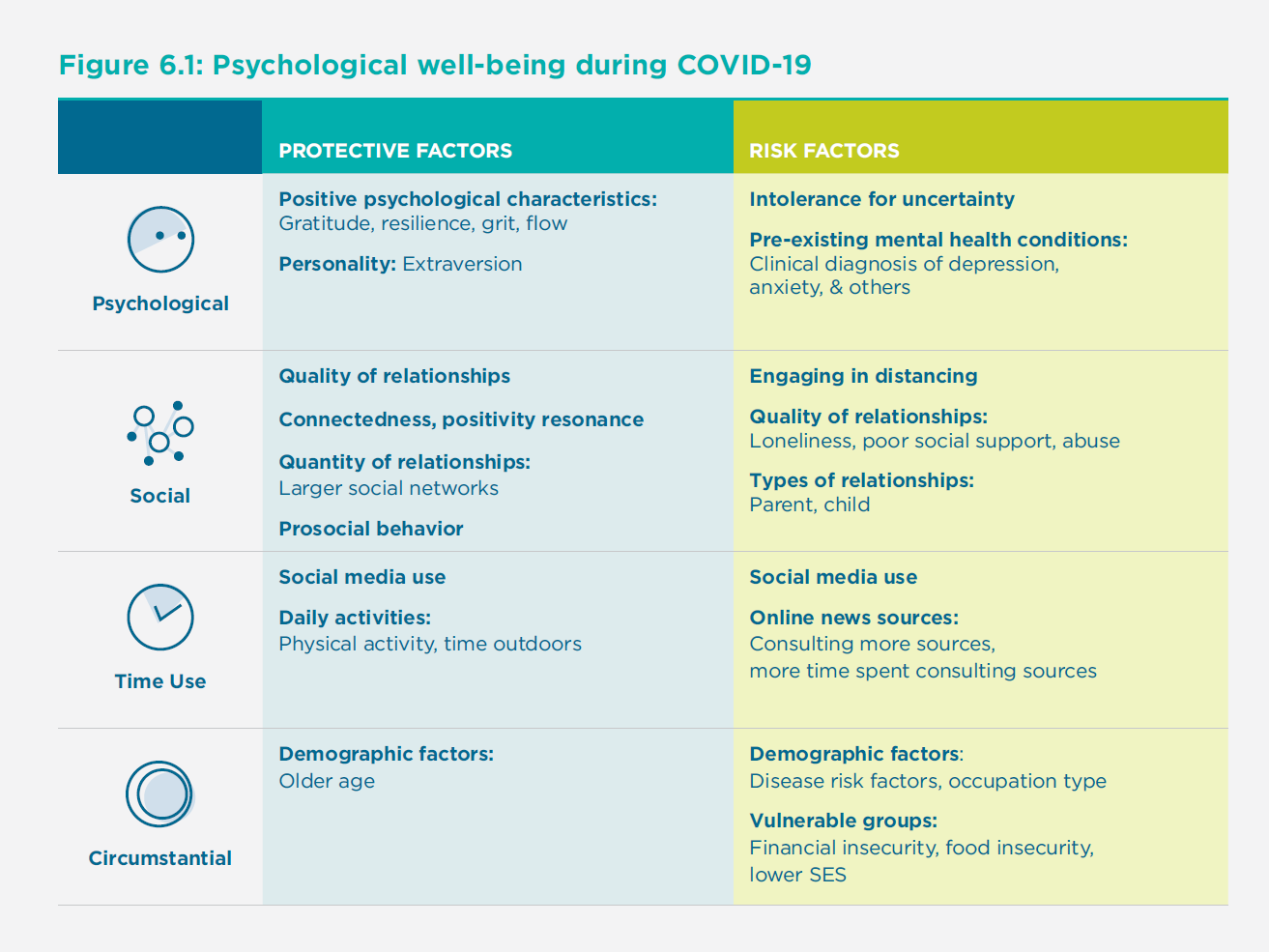
In many cases, digital connections — such as Zoom — provided a way to stay less isolated, and that was reflected by the lower levels of happiness in people without proper digital connections. Other factors that further diminished happiness were prior mental illness and a sense of uncertainty about the future.
Gallup’s Jon Clifton noted that loneliness has been greatly exacerbated by lockdowns: “Right now, over 300 million people in the world — that’s the same size as the United States — do not spend a single hour with a single friend.”
Some of the practices found to offset loneliness and help people cope were gratitude, grit, volunteering, previous social connections, exercise, and having a pet.
Work and Well-being
Work and its effect on happiness has been widely studied, and in 2020, the results around the globe were similar. Jan-Emmanuel De Neve of Oxford University led a team of scholars to look at how COVID-19 affected work and well-being and discovered that as unemployment rose, the effects were “devastating.” That was true regardless of income levels, global location, or gender, and resulted in a 10-30% drop in well-being, depending on the situation.
“At the start of the pandemic, 50% fewer jobs were being posted,” De Neve said. “As unemployment rose, job postings dropped. Not having a job or falling unemployed during a pandemic, mixed with half as few jobs available, is a toxic mixture.”
As people became unemployed, their loneliness escalated.
“There was about a 40% further impact on a person’s well-being if they didn’t have social support to rely on. People who [already] felt lonely were doubly impacted by losing their social networks at work.”
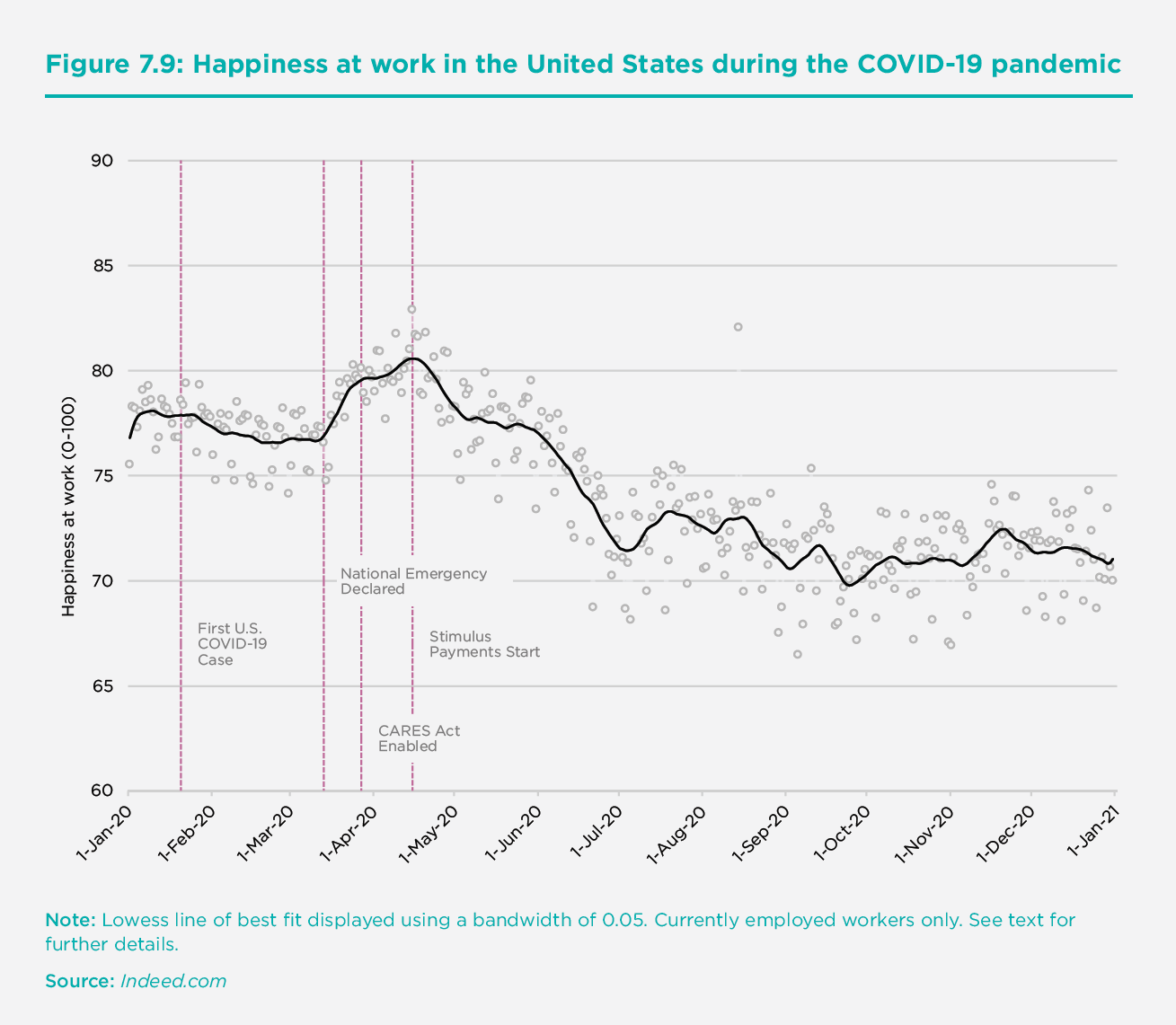
During the pandemic, supportive management and job flexibility became more important drivers of happiness at work, while such factors as purpose, achievement, and learning at work became less important. However, a sense of belonging, trust, and support remained unchanged, which De Neve said indicated that what makes workplaces supportive of well-being in normal times also makes them more resilient in hard times.
“Many more lessons can be learned from this on the future of work and how to build back happier,” he said.











